If you are thinking about your next vehicle purchase, you should consider an EV. There are now over 1.6 million EVs on the road in the U.S. and the market is booming, with 2019 sales totaling 325,000.
There are now over 175 models of electric vehicles on the road and automotive manufacturers are aggressively investing in EV technologies and rolling out new models with greater range each year. Plus, the nation’s public charging infrastructure has doubled over the past two years.








Most Americans drive less than 40 miles per day. The median driving range for model year 2020 electric vehicles was 258 miles, so, most Americans driving an all-electric vehicle can go multiple days without recharging.
The longest-range model 2020 EVs include Tesla's Model S Long Range Plus (416 miles) and Model 3 Long Range Performance (332 Miles), the Hyundai Kona (258 miles), and the Chevrolet Bolt (259 miles).
It's important to remember that EV driving range estimates are based on performance achieved under strictly controlled laboratory conditions. For the vast majority of EVs, range is higher for city, verses highway driving, as consumption increases at higher speeds. Daily driving routines can vary widely. It's best to choose a vehicle that can go the longest distance that you can afford.

Charge time depends upon the power source and the vehicle's charger capacity. Every EV has a its own battery charger that converts the AC electricity from the wall into DC, to charge the battery. A vehicle with a 10 kW charger and a 100-kWh battery pack takes approximately 10 hours to charge. Alternatively, a DC "fast charger" can charge to 80% capacity in about 30 minutes.

Charge time depends upon the power source and the vehicle's charger capacity. Every EV has a its own battery charger that converts the AC electricity from the wall into DC, to charge the battery. A vehicle with a 10 kW charger and a 100-kWh battery pack takes approximately 10 hours to charge. Alternatively, a DC "fast charger" can charge to 80% capacity in about 30 minutes.
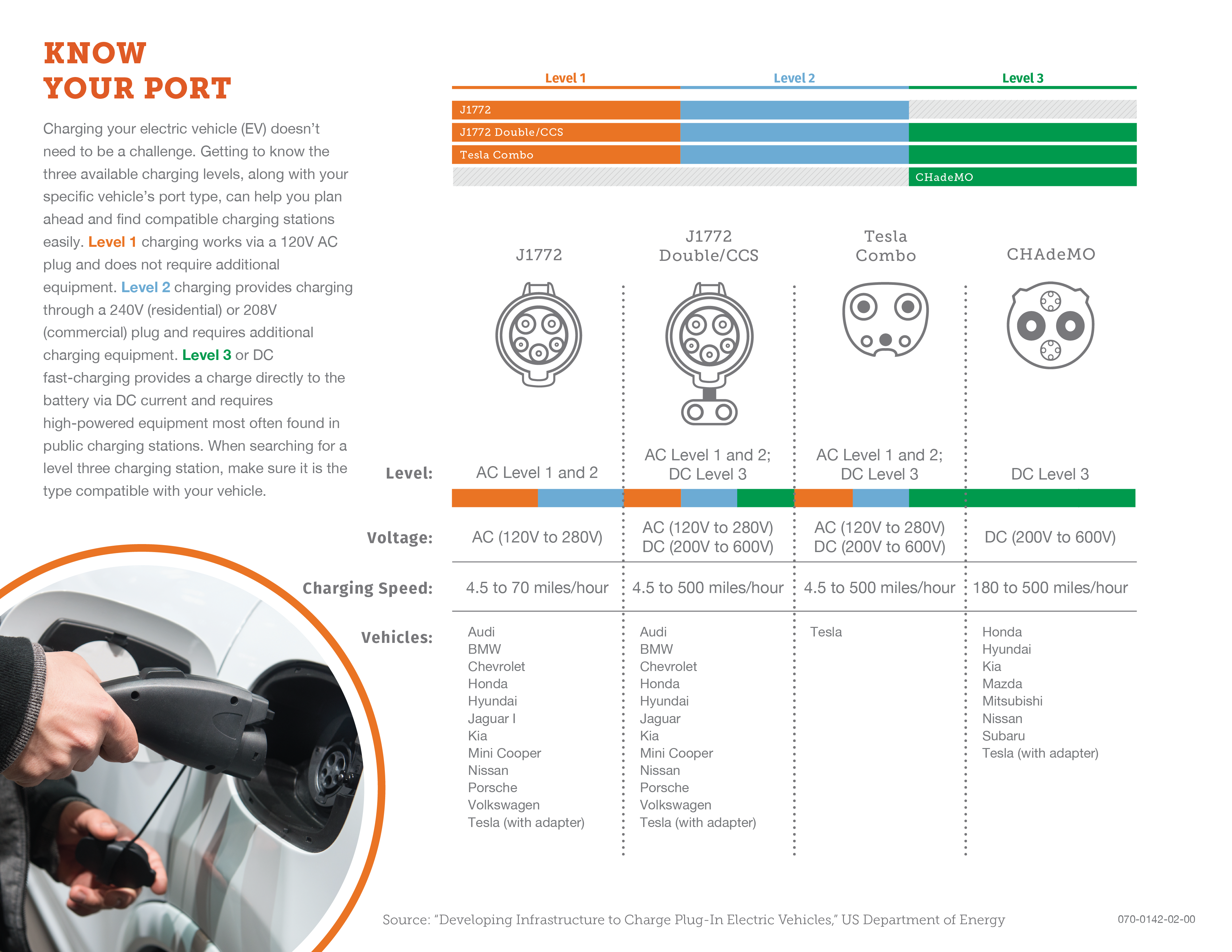
There are three major categories of chargers, based on the amount of power the charger can provide:
Level 1
This is the charging option that comes "standard" for most EVs. Charging occurs via a standard 120 V AC plug and does not require additional charging equipment. A Level 1 charger adds 2 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging, on average.
Level 2
Provides charging through a 240 V AC plug and adds 10 to 60 miles of range per hour of charging. This option requires the installation of an advanced EV charger and a dedicated 240 V circuit in your electric panel. You'll need to schedule installation by a licensed electrician/installer.
DC Fast-Charge
DC Fast-Charging, available at public charging stations, allows for much higher charging speeds because DC power is delivered directly to the electric vehicle's battery at higher power levels. A 50 kW DC fast charger can deliver 27 miles of range in about 10 minutes. In order to use a DC fast charger, your vehicle must have one of the three types of fast charging ports: CHAdeMO, CCS or Tesla. Not all plug-in hybrid electric vehicles can use a DC Fast charger.